- Common HTML tags
- Semantic HTML
- Attributes
- HTML comments
- Text and Headings
HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language. It is the standard markup language used to create web pages. HTML tags and elements are the building blocks of HTML documents. HTML tags define the structure and content of web pages, and HTML elements define the various parts of a web page, such as headings, paragraphs, links, images, and forms.
HTML Tags :-
HTML tags are used to define the structure and content of web pages. Each HTML tag consists of a pair of angle brackets (<>) and a tag name. For example, the <p> tag is used to define a paragraph, the <h1> tag is used to define a heading, and the <a> tag is used to define a hyperlink.
How to apply HTML Tags :-
HTML tags are applied to text by enclosing the text in the appropriate tag. For example, to create a paragraph, you would enclose the text in the <p> tag, like this: <p>This is a paragraph.</p>
Common HTML tags :-
Here are some common HTML tags that you are likely to encounter:-
<html>: Defines the start and end of an HTML document.
<head>: Defines the document's metadata, such as the title and description.
<title>: Defines the title of the document.
<body>: Defines the content of the document.
<p>: Defines a paragraph.
<h1> - <h6>: Defines headings of various sizes.
<a>: Defines a hyperlink.
<img>: Defines an image.
<ul>: Defines an unordered list.
<ol>: Defines an ordered list.
<li>: Defines a list item.
<table>: Defines a table.
<tr>: Defines a table row.
<td>: Defines a table cell.
<form>: Defines a form.
Semantic HTML :-
Semantic HTML refers to the use of HTML tags that convey meaning and structure to the content of a web page. Semantic HTML makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index the content of a web page, and it also makes the content more accessible to users with disabilities. Some examples of semantic HTML tags include <header>, <nav>, <main>, <section>, <article>, and <footer>.
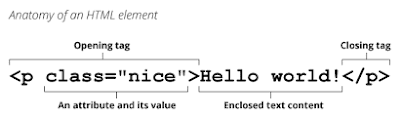
Attributes :-
HTML attributes provide additional information about an HTML element. Attributes are defined within the opening tag of an element, and they are usually written as name-value pairs. For example, the <a> tag uses the "href" attribute to specify the URL of the link, like this:
<a href="https://www.example.com">This is a link</a>
HTML comments :-HTML comments are used to add notes or explanations to the HTML code. HTML comments are not displayed in the browser, and they do not affect the appearance of the web page. HTML comments are enclosed in <!-- and -->, like this: <!-- This is a comment -->
Text and Headings :-
HTML provides a range of tags for formatting text and headings. Some of the most common tags for formatting text include:
<strong>: Makes text bold.
<em>: Makes text italic.
<u>: Underlines text.
<br>: Inserts a line break.
<hr>: Inserts a horizontal line.
Headings are defined using the <h1> - <h6> tags. The <h1> tag is used for the main heading of the web page, and the <h2> - <h6> tags are used for subheadings
I hope this overview helps you understand the basics of HTML tags and elements. Remember that HTML is just one part of web development, and there are many other technologies and concepts that are important for building modern websites. If you're interested in learning more about web development, I recommend exploring CSS, JavaScript, and web frameworks like React or Vue. Good luck!
The next topic for this course is Formatting Text. This section covers several important aspects of formatting text in HTML, including headings, paragraphs, line breaks, horizontal rules, and preformatted text. Understanding how to use these elements effectively is essential for creating visually appealing and easy-to-read web pages.

%20(1).jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpg)

.png)

%20(1).jpeg)
0 Comments
We love hearing from our viewers! Your comment is important to us. ❤️